Акмукабтаген аутолейцел
Acmucabtagene autoleucelМНН
Rec. INN (Recommended International Nonproprietary Name) — рекомендованное международное непатентованное наименование
Химическое название
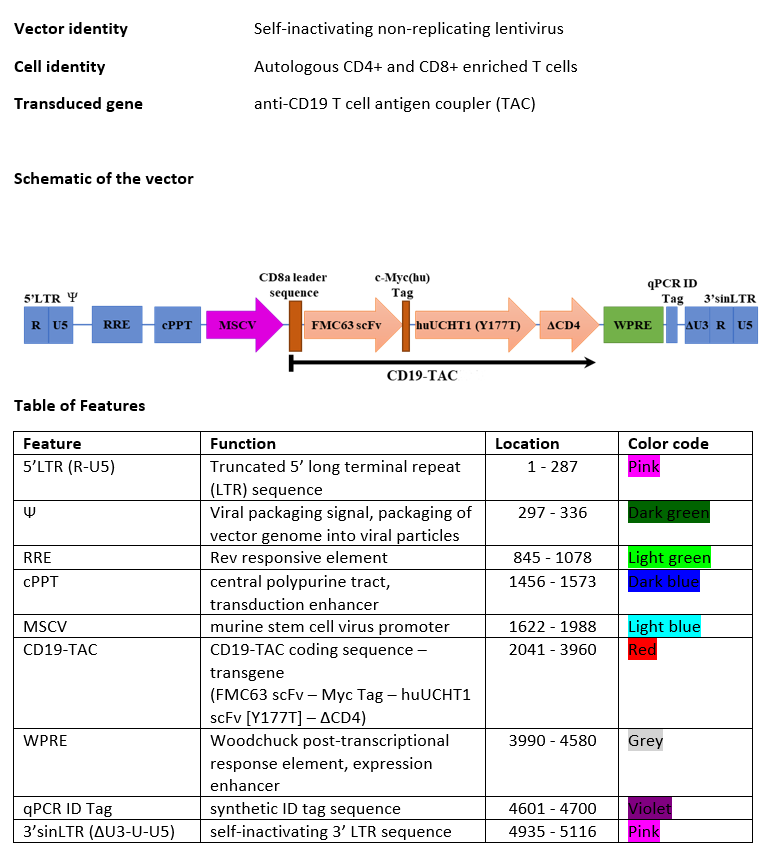
autologous T cells obtained from peripheral blood mononuclear cells by leukapheresis, transduced with a selfinactivating, non-replicating lentiviral vector, encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 (also known as B-Lymphocyte surface antigen B4) under control of the murine stem cell virus promoter. The transgene is a T cell antigen coupler (TAC) which has three components:
(i) an extracellular antigen-binding domain (anti-human CD19; FMC63 single chain variable fragment (scFv)), (ii) an extracellular T cell receptor (TCR) recruitment domain (antihuman CD3ε; UCHT1 scFv [Y177T]), and (iii) a membraneanchoring co-receptor domain that consists of the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of CD4. The vector genome is flanked by 5' and 3' long terminal repeats (LTRs) and contains also a ψ packaging signal, a Rev response element (RRE), a central polypurine tract (cPPT) sequence and the Woodchuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional regulatory element (WPRE). The leukapheresis material is enriched for CD4/CD8 T cells by positive immunoselection. T cells are cultured in the presence serum-free medium containing IL-2 and IL-7, and activated using a CD3/CD28/CD2 soluble activator. The T cells (>70%, generally ≥99%) are predominantly CD4 and CD8 T cells, with >10% viable CD3+TAC+ cells.
(i) an extracellular antigen-binding domain (anti-human CD19; FMC63 single chain variable fragment (scFv)), (ii) an extracellular T cell receptor (TCR) recruitment domain (antihuman CD3ε; UCHT1 scFv [Y177T]), and (iii) a membraneanchoring co-receptor domain that consists of the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of CD4. The vector genome is flanked by 5' and 3' long terminal repeats (LTRs) and contains also a ψ packaging signal, a Rev response element (RRE), a central polypurine tract (cPPT) sequence and the Woodchuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional regulatory element (WPRE). The leukapheresis material is enriched for CD4/CD8 T cells by positive immunoselection. T cells are cultured in the presence serum-free medium containing IL-2 and IL-7, and activated using a CD3/CD28/CD2 soluble activator. The T cells (>70%, generally ≥99%) are predominantly CD4 and CD8 T cells, with >10% viable CD3+TAC+ cells.
Структура

Иностранные названия
- Acmucabtagenum autoleucelum (латинское)
- Acmucabtagene autoleucel (английское)
- Acmucabtagène autoleucel (французское)
- Acmucabtagén autoleucel (испанское)
Подробнее по теме
Узнайте дополнительные сведения о действующем веществе Акмукабтаген аутолейцел:
